How To Prepare a Reliable Disaster Recovery Plan

“The time to prepare for disasters is before they happen” (Stephen Matheson, Vice President of Product at BridgeHead)
Given how reliant we all are on our IT infrastructure, it will come as no surprise to learn that one of the worst things that can happen to a business is for a failure to occur in that department. Whether it’s fire, floods, or hacking, being taken offline can spell a serious period of trouble for most organisations. In the time it takes to get back up and operational projects can be delayed, the quality of work can suffer, or worst of all, everything is put on hold for months while data is recreated. All of this can lead to strained relationships with both customers and suppliers and potentially the end of the business.
A Disaster Recovery Plan is the pre-planned process a company will turn to when disaster strikes to ensure that a short-term problem does not become a permanent one.
Here are five simple tips for what you need to consider when drawing one up.
- Have a response checklistThe response checklist is a detailed breakdown of which employees should be contacted and what they should do in the event of a disaster. These should cover everything from who phones your IT support company to who puts out the fire or organises the evacuation drill. Ideally, these responses should be practiced. It’s no good telling someone they have to turn off the building’s water in the event of a flood if they don’t know where to do that.
- Have a data backup planAll company data needs to be backed up, as regularly as possible. How this is done will depend on how vital that data is to the operational capabilities of your business but should happen at least once a day. Look at your company carefully and decide which information is vital and which can safely be lost. You don’t need to back up all your client emails if you also keep other records of their projects for instance.Data is a business asset and has real value. The more important the data, the more strictly and safely that data needs to be backed up. Can you do it yourself on a hard disk that the secretary takes home, or do you need a full-scale external, cloud-based solution?
- How are you going to tell your clients?While it’s usually a good idea to keep drama and difficulties far away from your clients, in this instance it may be important to tell them what is going on to explain any delays they may be about to experience and how you are planning to meet their orders. In addition, provide them with any alternate contact details.Your plan should detail exactly how that is going to happen. Having pre setup and approved email addresses and telephone numbers organised will save a lot of time and frustration until your company is back on its feet.
- Cost considerationsYour plan should also take into account the cost considerations of setting things up anew. Will you need to buy new servers? Do you need to bring in IT experts to recover data? The money for this should be set aside and available as every day you delay your recovery is another step closer to bankruptcy.Speak with your accountant as to how you can finance this fund, or whether insurance options may be a financially viable option for your company.
- Vital document and data storage
On top of all of this, your Disaster Recovery Plan should also detail where copies of all the most vital information will be stored and how they can be retrieved. This should be a safe and secure offsite location. Keys and access codes need to be kept in a third location as well.
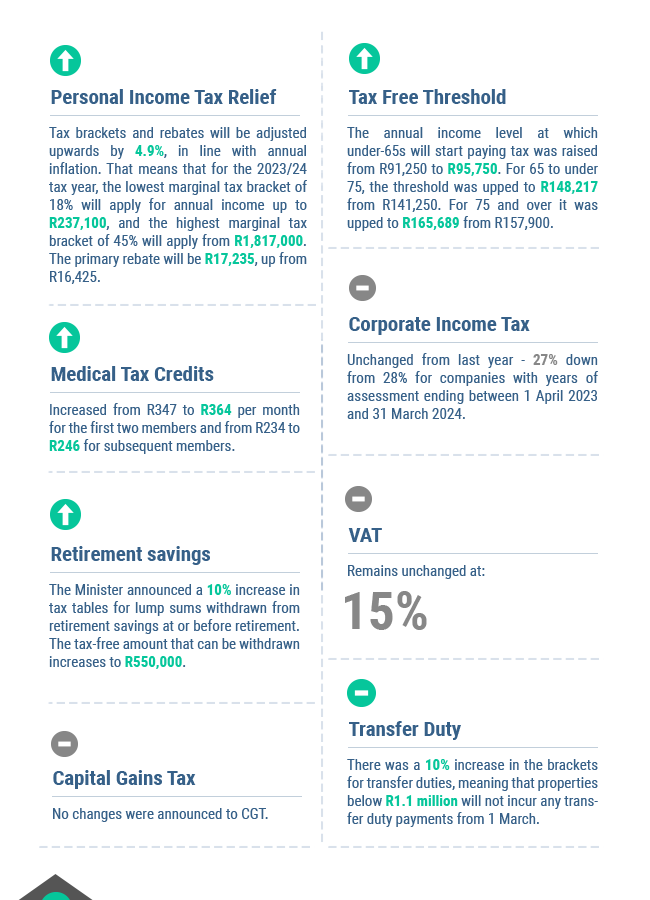
Budget Speech 2023 | How it affects you and your business

The 2023 budget speech delivered by Finance Minister Enoch Godongwana brought a fair amount of good news for South Africans.
There will be support for households and businesses installing renewable energy, no income tax increases were announced, and the fuel levy remains unchanged, taking some pressure off people’s budgets.
However, the Minister could not avoid acknowledging that the problems at Eskom are a big challenge to the country’s growth prospects.
“The lack of reliable electricity supply is the biggest economic constraint,” Godongwana said.
He therefore announced that government would be taking over a big portion of Eskom’s debt to take some pressure off the utility, and that a number of steps were being taken to restructure the local electricity industry.
“Establishing a competitive electricity market will enable South Africa to ensure a stable, uninterrupted power supply as it transitions to a clean energy future,” National Treasury stated in its budget review.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Your Tax Deadlines for February 2023

- 7 February – Monthly Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE) submissions and payments
- 27 February – Excise Duty payments
- 28 February – Value-Added Tax (VAT) electronic submissions and payments & CIT Provisional payments where applicable.