Your Tax Deadlines for April 2025

- 01 April – Start of the 2025/26 Financial Year
- 07 April – PAYE submissions and payments
- 25 April – VAT manual submissions and payments
- 29 April – Excise duty payments
- 30 April – VAT electronic submissions and payments, & CIT Provisional Tax payments where applicable.
Budget 2025: Your Tax Tables and Tax Calculator

Budget 2025, if adopted by Parliament, will effectively bring about an increase in personal income tax by not adjusting the tables for tax rates, rebates and credits, while also implementing substantial increases in ‘sin’ taxes and introducing a 0.5% VAT increase on 1 May 2025 and another 0.5% increase effective 1 April 2026.
This selection of official SARS Tax Tables and other useful resources will help clarify your tax position for the new tax year.
Individual taxpayers: Tax tables unchanged since 2023
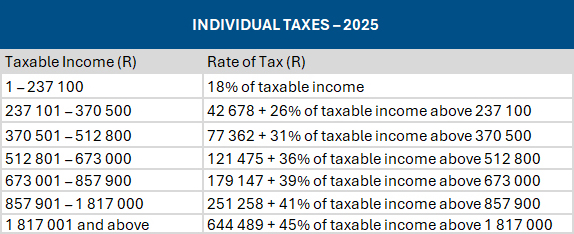
Source: SARS
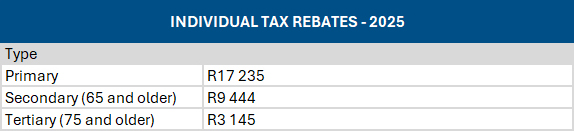
Source: SARS
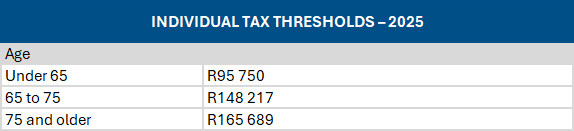
Source: SARS
Sin taxes raised
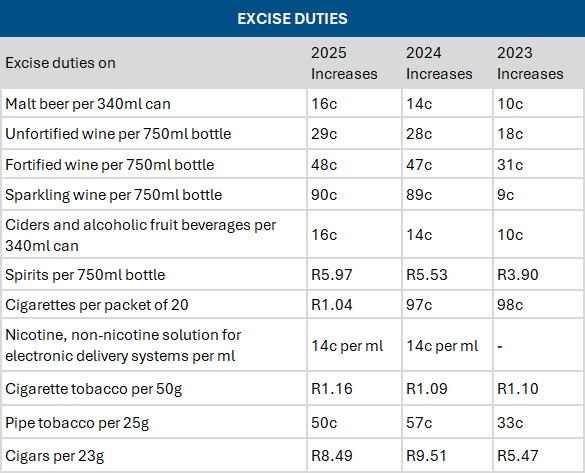
Source: Adapted from Budget 2025 People’s Guide
Businesses: Corporate tax rates unchanged
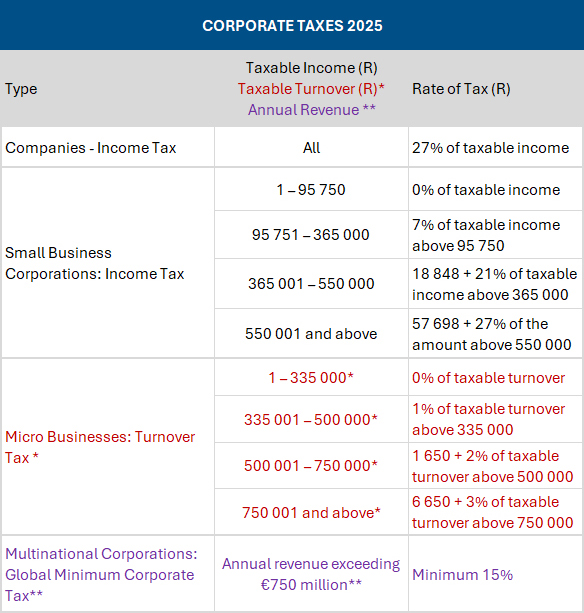
Source: Adapted from SARS Budget Tax Guide 2025
Proposed VAT increases
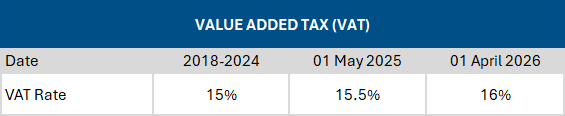
Source: Adapted from Budget 2025 People’s Guide
Transfer duty: 10% upward adjustment from 1 April
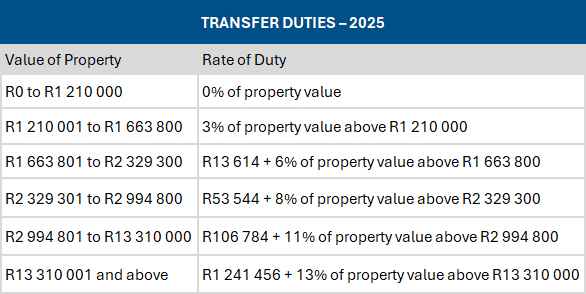
Source: SARS’ Budget Tax Guide 2025
How much will you be paying in income, petrol and sin taxes?
Use Fin 24’s four-step Budget Calculator here to find out the monthly and annual impact on your income tax, as well as what you will be paying in fuel and sin taxes.
Budget 2025: How It Affects You and Your Business

“… the economy needs to grow much faster and in an inclusive manner. This is the central objective of the current administration.” (Finance Minister Enoch Godongwana – Budget 2025)
The tabling of Finance Minister Enoch Godongwana’s fourth Budget in February was marked by an unprecedented three-week postponement, following a deadlock around the original Budget proposal to increase VAT by 2%.
A revised Budget, finally tabled on 12 March, proposed a 0.5% increase from 1 May 2025, with a second 0.5% VAT increase from 1 April 2026 – but the proposal was still not enough to satisfy most other political parties.
In his Budget Speech, the finance minister called the Budget proposals “a bold and pragmatic approach” to ensure the economy grows “much faster and in an inclusive manner”. He admitted that the economy has stagnated for over a decade, with GDP growth averaging less than 2%, while forecasts for medium-term GDP growth are a dismal 1.8%.
While the powers that be attempt to reach consensus on the Budget 2025 proposals, businesses and individuals in South Africa will find little support from the fiscus to survive these low-growth economic conditions.
This is evident from our overview below of the most pertinent Budget 2025 proposals. In a nutshell, the finance minister is trying to cover another substantial Budget shortfall by directly and indirectly increasing the tax burden on corporate and individual taxpayers.
Budget proposals that will impact you
- The 0.5% VAT increases proposed for 2025 and 2026 will impact every South African, while disproportionately affecting lower-income households strained by high electricity costs, inflation and interest rates in a weak economy. To alleviate their impact on poor households, the list of zero-rated food items is extended to include canned vegetables, dairy liquid blends, and organ meats from sheep, poultry and other animals.
- Personal income tax brackets will not be adjusted for inflation for a second year running. This means that, like last year, individuals who receive a salary increase will again pay more tax, and could be pushed into a higher tax bracket.
- No inflation adjustments were proposed for tax rebates or medical tax credits – which once again translates into more tax payable by individuals.
- Above-inflation increases in the excise duties on alcohol (6.75%) and tobacco (4.75 – 6.75%) are no surprise. This means that with immediate effect, the duty on:
- a 340ml can of beer increases by 16c
- a 750ml bottle of unfortified wine goes up by 29c
- a 750ml bottle of fortified wine goes up by 48c
- a 750ml bottle of spirits will increase by R5.97
- a 23g cigar goes up by R8.49
- a pack of 20 cigarettes rises by R1.04
- vaping products increase by 14c per millilitre.
- Changes to the rules regarding the tax treatment of cross-border retirement funds are proposed.
- A one-year extension in the R370 social relief of distress (SRD) grant and above-inflation increases ranging from R30 to R130 per month in other social grants will provide minimal relief to the poorest South African households.
- SARS has been allocated R3.5 billion this year and an additional R4 billion over the medium term to enhance its tax collection capabilities, so taxpayers can expect increased scrutiny and administration.
Budget proposals that will impact your business
The 0.5% VAT increases proposed for 1 May 2025 and 1 April 2026 will certainly impact all companies in South Africa’s struggling economy, with a disproportionately negative impact on the small and micro businesses that are crucial to economic growth.
- VAT hikes directly raise the cost of goods and services, impacting competitiveness and profitability.
- Higher prices resulting from the VAT increase will reduce consumer purchasing power in an already-constrained economy.
- The VAT increase could trigger inflationary pressures, further eroding household incomes and potentially forcing an interest rate hike.
- Two VAT increases over two years will also result in a significant administrative burden on businesses to implement the required changes to their systems.
- Carbon taxes increased from R190 to R236 per tonne on 1 January, while the temporary incentive for renewable energy introduced in 2023 has not been extended.
- From 1 April 2025, the formula to calculate the employment tax incentive and the eligible income bands will be adjusted.
- It is proposed that the sunset date for the urban development zone tax incentive be extended by five years to 31 March 2030.
- The Budget proposes to cancel the inflationary increase in the health promotion levy, and that the ad valorem excise duties on smartphones are limited to higher value phones.
Some good news
- The general fuel levy and the Road Accident Fund levy will not be increased again this year, providing tax relief of R4 billion. However, the carbon tax on fuel and diesel will increase. Budget 2025 also proposes an adjustment to the diesel refund for the primary sector for the next tax year.
- Property buyers will benefit from an upward adjustment of 10% in transfer duty brackets from 1 April 2025.
- A R1 trillion investment over the next three years in public infrastructure spending, focussed on transport and logistics, energy, and water and sanitation, should positively impact on the economy.
- Besides the proposals detailed above, Budget 2025 made no mention of a wealth tax or the National Health Insurance (NHI).
- In a media interview following the Budget Speech, the minister said that if the economy does well, the VAT increase in 2026 may not be necessary.
